
See: Description
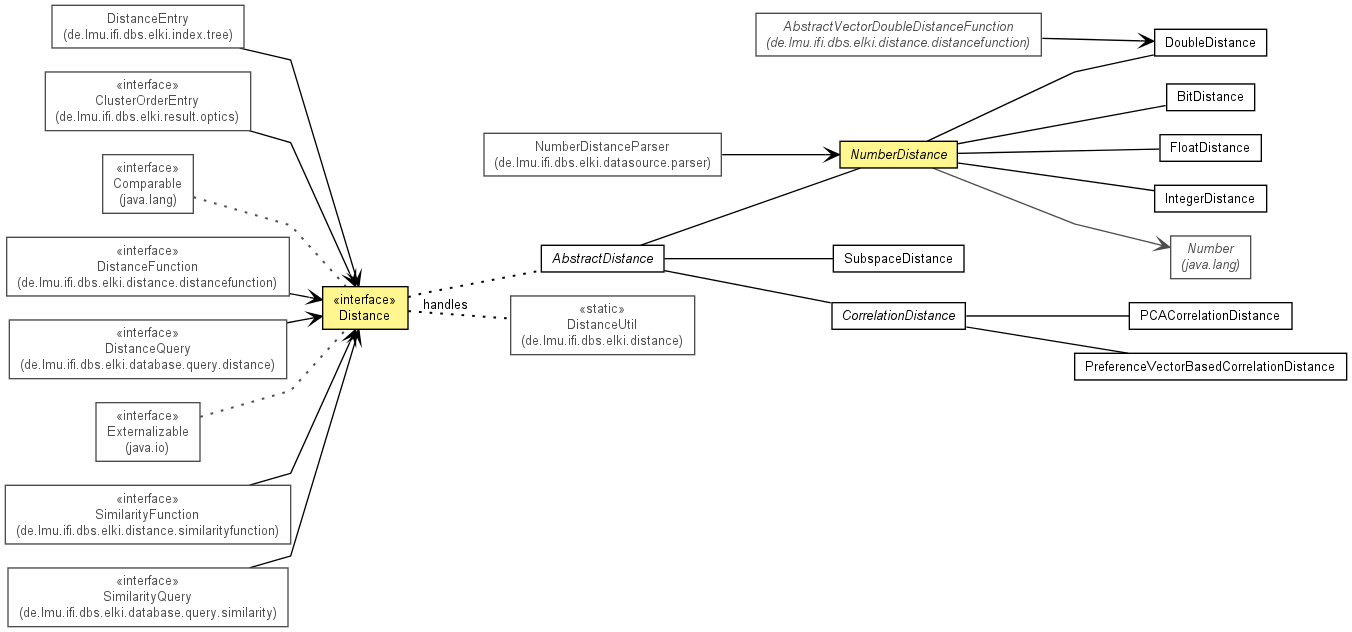
| Interface | Description |
|---|---|
| Distance<D extends Distance<D>> |
The interface Distance defines the requirements of any instance class.
|
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| AbstractDistance<D extends AbstractDistance<D>> |
An abstract distance implements equals conveniently for any extending class.
|
| BitDistance |
Provides a Distance for a bit-valued distance.
|
| CorrelationDistance<D extends CorrelationDistance<D>> |
The correlation distance is a special Distance that indicates the
dissimilarity between correlation connected objects.
|
| DoubleDistance |
Provides a Distance for a double-valued distance.
|
| FloatDistance |
Provides a Distance for a float-valued distance.
|
| IntegerDistance |
Provides an integer distance value.
|
| NumberDistance<D extends NumberDistance<D,N>,N extends Number> |
Provides a Distance for a number-valued distance.
|
| PCACorrelationDistance |
The correlation distance is a special Distance that indicates the
dissimilarity between correlation connected objects.
|
| PreferenceVectorBasedCorrelationDistance |
A PreferenceVectorBasedCorrelationDistance holds additionally to the
CorrelationDistance the common preference vector of the two objects defining
the distance.
|
| SubspaceDistance |
The subspace distance is a special distance that indicates the dissimilarity
between subspaces of equal dimensionality.
|
Distance values, i.e. object storing an actual distance value along with comparison functions and value parsers.
Distances follow a factory pattern. Usually, a class will have a static instance
called FACTORY that can be used to obtain e.g. infinity or zero distances
as well as parse a string value into a new distance value.