Package de.lmu.ifi.dbs.elki.database.ids
Database object identification and ID group handling API.
See:
Description
Package de.lmu.ifi.dbs.elki.database.ids Description
Database object identification and ID group handling API.
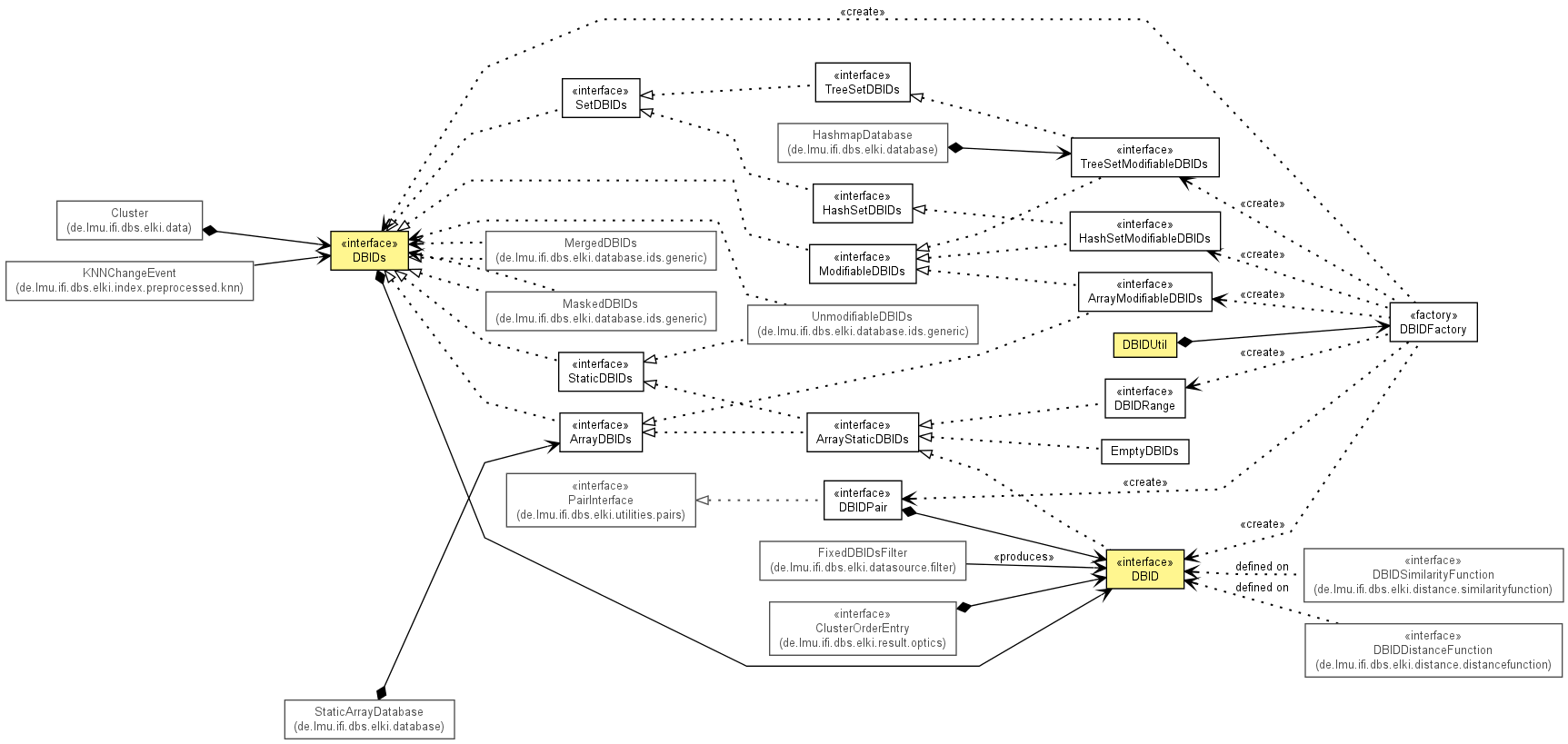
Database IDs (short: DBID) in ELKI are based on the factory pattern, to allow replacing
the simple Integer-based DBIDs with more complex implementations, e.g. for use with external
databases or to add tracking for debugging purposes. This also allows adding of more efficient
implementations later on in a single place.
DBID interface:
The DBID object identifies a single object.
The DBIDs hierarchy contains classes for handling groups (sets, arrays) of IDs, that can
be seen as a two-dimensional matrix consisting
StaticDBIDs are structures that cannot support
modifications, but thus can be implemented more efficiently, for example as Interval. They are
mostly used by the data sources.
These interfaces cannot be instantiated, obviously. Instead, use the static
DBIDFactory.FACTORY, which is also wrapped in the DBIDUtil class.
Examples:
DBIDs allids = database.getIDs();
// preallocate an array of initial capacity 123
ArrayModifiableDBIDs array = DBIDUtil.newArraySet(123);
// new DBID hash set with minimum initial capacity
ModifiableDBIDs hash = DBIDUtil.newHashSet();
// initialize a tree set with the IDs of the database.
ModifiableDBIDs tree = DBIDUtil.newTreeSet(database.getIDs());
// add all DBIDs from the hash
tree.addDBIDs(hash)
Utility functions:
The static DBIDUtil class provides various utility functions, including:
Generic utility classes:
MergedDBIDs
allows virtual concatenation of multiple DBIDs objects.
MaskedDBIDs
allows masking an ArrayDBIDs with a BitSet.


